To use a Shared Folder on your virtual machine:
1. Use the VirtualBox GUI to add a folder, located on your host (“real”) computer to the list.
This will be the folder that you want to use for sharing and which will be visible on your “guest” machine.
The Shared Folders are available from the Devices menu or from the bottom icons (right-click the little cyan folder icon).
![]()
Locate and add the folder which you want to access from both the real and virtual computers
2. On the virtual machine make the shared folder available/visible to the “guest” OS. On Linux this involves the mount command.
For example:
On the host (real) computer, the directory that you want to use for sharing is called /opt/datadir.
You want this shared directory to appear as “/data” on your virtual machine.
Assuming that you followed the above instructions and added the folder to the Virtual Box list of shared folders and you called it “mydata”, you may now execute on your virtual machine the following command:
# sudo mount -t vboxsf mydata /data
This should mount your host /opt/datadir folder (called “mydata”) to the /data folder of your guest OS. (Of course, as with any normal mount command you must have the /data directory created, empty and available for writing already there, before you do the mount).
The crucial point here is creating the Shared folder in VirtualBox and naming it some name (mydata in the example above). This creates a virtual device, known by that name and of the fs type “vboxsf”, thus making it available for standard mounting by the mount command.
/opt/datadir --> "mydata" --> /data
Once you have the folder mounted you can find it’s entry in /etc/mtab and transfer it to /etc/fstab – this way your folder will be always auto-mounted when you start your VB machine 🙂
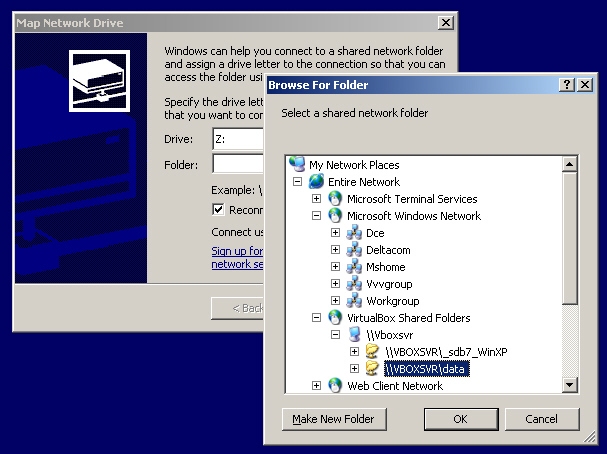
NOTE: On Windows the equivalent of the above is achieved by using the “Map Network drive” command from the Windows Explorer “Tools” menu (find your shared folder under the “VirtualBox Shared Folders” network place in Entire Network).
Sometimes it may happen that you would be unable to access (as a user) some of your shared folders inside the VBox machine. I mean – not even read access, i.e. can’t even cd to the shared dir.
If that happens go and check ‘world’ permissions of the folder on the HOST machine – there must be at least read permissions if you want to be able to see the contents of the folder on the GUEST (as a user – root will always have access of course). To fix this problem, do (on the HOST PC):
$ sudo chmod a+r /the_shared_dir
$ sudo chmod a+r /the_shared_dir